TEACHING AND LEARNING APPROACH
DID YOU KNOW?
Hermann Ebbinghaus
German philosopher (1850-1909), generally considered to be the father of the experimental psychology of learning. He applied experimental methods to the study of memory and learning.
He is also associated with the theory of associationism, which looks at “how facts or ideas can be associated with each other in people’s thoughts, thus leading to a type of learning”.
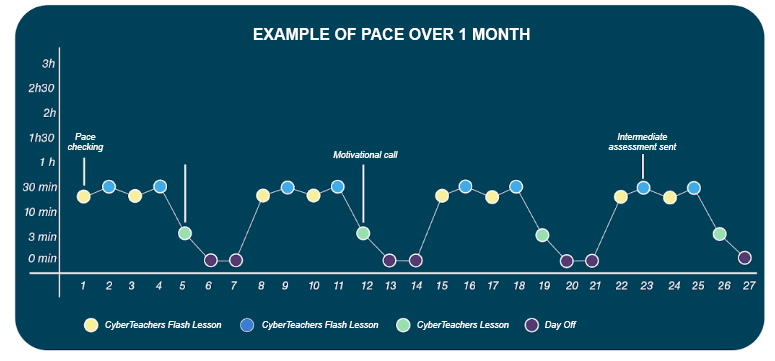
ASSIMILATION MECHANISM
As this graph shows, when you memorise something for the first time, you will probably forget it very quickly. The curve (light blue) is therefore fairly steep. If you repeat it once a short time later (red curve) …you can see that the information doesn’t disappear as quickly: the curve isn’t as steep. After a number of repetitions, the curve flattens and the information is more and more firmly anchored in our memory. As time goes by, the information is more firmly anchored and repetitions can be farther apart.
THE SPACING EFFECT
The spacing effect refers to the fact that long term memorisation is more effective when a period of learning is divided into a number of sessions rather than taking place all at once. Spaced repetition is thus more effective than cramming in terms of long-term learning.
ASSIMILATION MECHANISM